[paper] ECAPA-TDNN: Emphasized Channel Attention, Propagation and Aggregation in TDNN Based Speaker Verification
본 포스트는 Speaker Verification 분야 높은 성적을 거둔 논문에 대한 내용이다.
벨기에 IDLab에서 연구되어 Interspeech 2020에 발표되었으며, VoxCeleb2 데이터셋[Chung18]에서 높은 성능을 보여 큰 관심을 받았다. 이는 x-vector[Snyder18] 이후 화자확인 분야에서 baseline이 되는 모델로 선정되며, RawNet3[Jung22]를 비롯한 차후 모델에도 큰 영향을 끼쳤다.
Abstract에 따르면, 기존 x-vector[Snyder18] 모델 구조에 세가지 변화를 주었다고 한다. 세 가지 변화는 핵심 요약에 기술되어 있다.
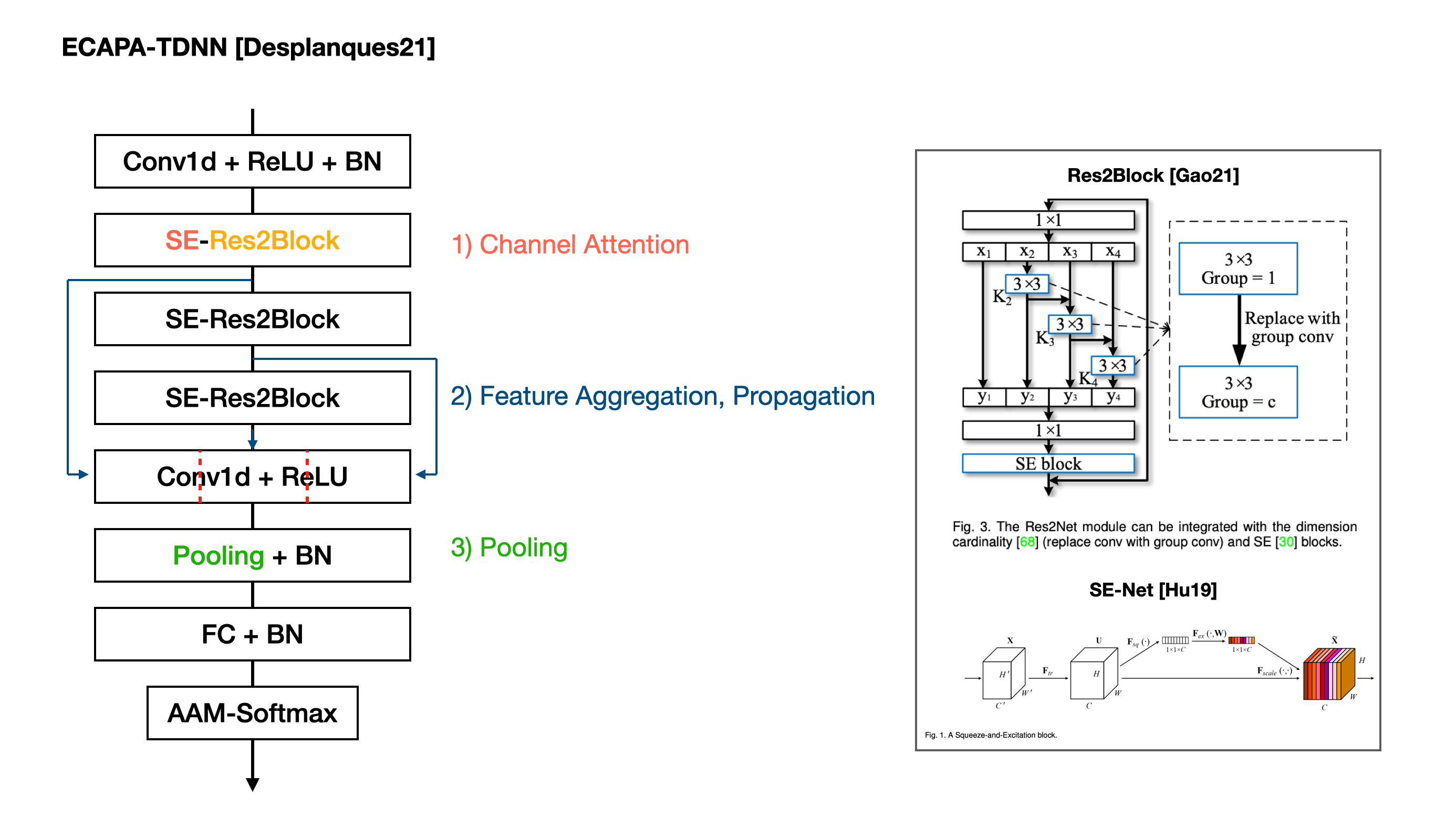
핵심 요약
- Channel Attention
- SE block 모듈 도입하여 channel interdependencies 향상
- Res2Net과 같은 skip connection 도입
- Feature Aggregation, Propagation
- 다른 계층 (hierarchical) 특징을 활용하는 방법 도입
- channel- and context-dependent statistics pooling
- 프레임을 더 자세하게 반영하는 풀링 방법 도입
Abstract X-vector achitecture is TDNN. Statistics Pooling project utterance into speaker embeddings ECAPA-TDNN has 3 enhancement to X-vector
- Skip connection (Resnet) and Squeeze-and-Excitation (SENet) modules are introduced to model channel interdependencies. The SE block expands the temporal context of frame layer by rescaling the channels according to global properties of the recording
- Aggregating and Propagating features of different hierarchical levels. Originally, features operate separately in layers
- Statistics Pooling is replaced with Channel-dependent frame attention.
Introduction
bottleneck -> low dimensional speaker embedding
Consine Similarity or PLDA training compares 2 embeddings
Additive Angular margin optimization, ResNet aprroaches in frame-level layer, temporal self-attention are introduced in X-Vector
Statistics Pooling (projects variable length input into a fixed-length representation)
AAM (good at image detection) ResNet (enable the back-propagation faster and avoid vanishing gradient) self-attention (focus on important frames)
DNN speaker recognition systems (Baseline)
Extended-TDNN x-vector
The initial frame layer of X-vector has 1 dimensional dilated convolutional layer interleaved with dense layers
Residual Connection
frame layer -> attentive statistics pooling layer -> 2 FC layer
dilated layer (gradually build up temporal context)
pooling layer (calculates mean and standard deviation of the final frame layer features)
FC layer (one creates bottleneck)
ResNet-based r-vector
ResNet18 and ResNet34 architecture
The convolutional frame layer process features as a 2-dimensional signal
Proposed ECAPA-TDNN architecture
frame-level and pooling-level enhancements
3.1. Channel- and context-dependent statistics pooling
enhance X-vector + self-attention by extending temporal attention mechnism into the channel dimension (to focus on speaker characteritics, not on time instances)
W is a parameter that belongs to R*C, where C denotes Channels. ReLU() transforms this into channel-dependent self-attention score
Then scalar score “e” is normalized over all frames (channel-wise across time)
The normalized “e”, which is “a”, represents self-attention score of each frame given the channel (attention reduces parameter and risks of overfitting)
And calculate the weighted statistics (mean and standard deviation) of channel c by multiplying self-attention score
Weighted Statistics are concatenated to create final output of pooling layer
(now self-attention can look at global properties)
3.2. 1-Dimensional Squeeze-Excitation Res2Blocks
enhance temporal context of x-vector 15 frames by rescaling the frame-level features with SE blocks
(SE block may model global channel interdependencies)
Squeeze - calculate mean vector of z of the frame-level features across time domain
Excitation - ReLU and Sigmoid to create s, which makes a bottleneck layer C*R (channel and dimensionality) s has weights between 0 and 1, then s is applied to original input through channel-wise multiplication
Using SE-block after each dilated convolution is recommended
SE-Res2Block suggests “dense layer + dilated convolution + dense layer” with a context of 1 frame
1st dense layer reduce dimension, 2nd one restore the dimension
Then Res2Net module enhances the central convolutional layer to process multi-scale features by constructing hierarchical residual like connections within
3.3. Multi-layer feature aggregation and summation (MFA)
enhance X-vector using last frame-layer as pooling by concatenating all feature maps of SE-Res2Blocks
Or, using SE-Res2BLock outputs and initial convolutional layer as input for each frame layer block
(summation of the feature maps instead of concatenation to reduce parameter)